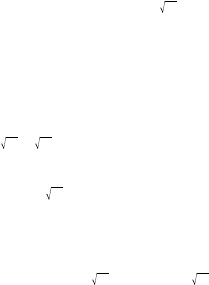
E-30
k Order of Operations
Calculations are performed in the following order of prec-
edence.
1 Coordinate transformation: Pol (
x, y), Rec (r,
θ
)
2 Type A functions:
With these functions, the value is entered and then the
function key is pressed.
x
3
, x
2
, x
Ҁ1
, x!,
° ’ ”
m
,
m
1
,
m
2
,
n
Angle unit conversions (DRG')
3 Powers and roots:
^
(x
y
),
x
4 a
b
/c
5 Abbreviated multiplication format in front of π, e (natural
logarithm base), memory name, or variable name: 2
π,
3
e, 5A, πA, etc.
6 Type B functions:
With these functions, the function key is pressed and
then the value is entered.
,
3
, log, In, e
x
, 10
x
, sin, cos, tan, sin
Ҁ1
, cos
Ҁ1
,
tan
Ҁ1
, sinh, cosh, tanh, sinh
Ҁ1
, cosh
Ҁ1
, tanh
Ҁ1
, (Ҁ)
7 Abbreviated multiplication format in front of Type B func-
tions: 2
3, Alog2, etc.
8 Permutation and combination:
nPr, nCr
9 ҂, Ö
0 ѿ, Ҁ
• Operations of the same precedence are performed from
right to left.
e
x
In 120 → e
x
{In( 120)}
•Other operations are performed from left to right.
• Operations enclosed in parentheses are performed first.
•When a calculation contains an argument that is
a negative number, the negative number must be
enclosed within parentheses. The negative sign (–) is
treated as a Type B function, so particular care is
required when the calculation includes a high-priority
Type A function, or power or root operations.
Example: ( –2)
4
= 16
–2
4
= –16


















