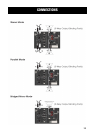
11
Clip Limiter
Clipping is the result of an amplifier running into a power supply limitation. The maximum
output voltage that any amplifier can produce is limited by its power supply. Attempting to
output a voltage (or current) level that exceeds the power supply results in a “flattenin” effect
on the signal, making it’s waveform look cut off or “clipped”. A clipped waveform exhibits
extreme harmonic distortion, dominated by large amplitude odd-ordered harmonics and
making it sound harsh or dissonant.
The clip limiter detects this and reduces the gain to minimize the amount of overdrive. To
preserve as much of the program dynamics as possible, limiting reduces the average program
level until peaks barely clip. Each channel has its own clip limiter, and you can switch it on or
off.
When driving full-range speakers, clip limiting reduces high frequency distortion caused by
bass overload. It also protects higher frequency drivers from excess overdrive and harsh
clipping harmonics.
HPF (Hi-Pass Filter)
A filter having a passband extending from some finite cutoff frequency (not zero) up to infinite
frequency. Also known as a low-cut filter. HPF rolls off signals below 30Hz or 50Hz, removing
the frequencies below the selected roll off. Reproduction of the signal’s bass portion is thus
optimized, since ultra-low, distracting frequencies are eliminated, and more power is available
for the reproduction of the wanted segment of the signal.
You should set up the filters so they best suit the frequency response of your speakers, since
some speakers are particularly sensitive to over-excursion. The 50Hz filter works well with
most compact full-range speakers.
SETUP