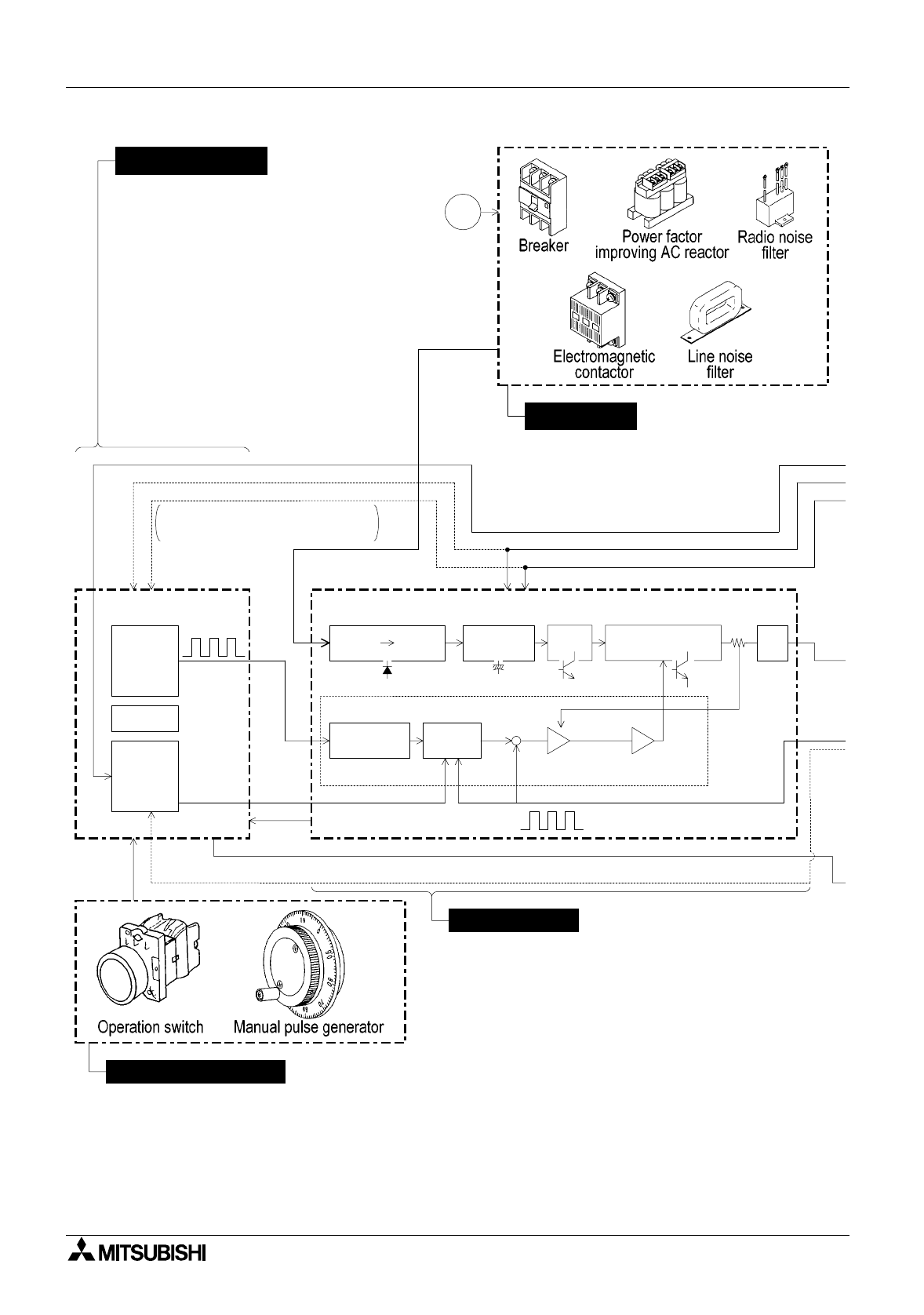
Positioning Control Components of Positioning Control and Their Roles 3
3-2
Positioning
command
control
Deviation
counter
Smoothing
circuit
Inverter
PWM (pulse width
modulation) control
Current
control
Speed
command
Feedback
current
Feedback pulse
Servo amplifier
R
Regenerative
brake
Pulse
magnification
(Electronic gear)
Dynamic
brake
Counter clear
Zero point
return
control
Parameter
Command
pulse
Position controller
Servo
ready
Main circuit
In some types, the limit switch signal
is wired to the position controller.
Zero point signal (PG0)
Converter
AC DC DC DC AC
Near point dog signal
Position controller
Power board
AC power
supply
Operation equipment
Servo amplifier
• Outputs the positioning speed
and the movement quantity in
command pulses to the servo
amplifier.
• Transfers signals between the
programmable controller.
• Controls return to the zero point.
• Improves the power factor
and cuts noise.
• Protects the power circuit.
• Rectifies the AC power of the main circuit into
the DC power in the converter, and smooths it in
the smoothing circuit.
When the DC power is converted into AC power
in the inverter, the current supplied to the servo
motor is changed by the PWM (pulse width
modulation) control in the control circuit.
• The deviation counter receives and counts the
command pulses from the positioning controller,
subtracts the feedback pulses from them, then
drives the servo motor until the accumulated
pulse number becomes 0.
• Give inputs for manual/automatic
mode, start/stop, zero point return
command, manual forward rotation/
reverse rotation and manual pulse
generator to the positioning
controller.
