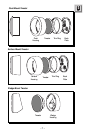
• Sound radiated from a “point source” has the most optimum stereo imaging
because the separation of the acoustical centers between the midrange and
tweeter for each channel is at the optimum. Figure 2-A describes a
horizontal speaker alignment. In a closed environment such as an
automobile, horizontal speaker alignment can cause severe amplitude and
phase differences which will degrade not only the imaging, but also the
frequency response. This is due to the path length differences between the
midrange and tweeter. Figure 2-B displays a vertical alignment between the
midrange and tweeter. With a vertical alignment, the path length difference
between the midrange and tweeter are reduced to a minimum. The result
is a negligible difference in path lengths between the midrange and tweeter
regardless of the proximity of the listener to the speakers. Mounting the
speaker with minimum path length difference will ensure the best staging
and imaging possible from your audio system.
I
NSTALLATION
Mounting the Midrange
– 6 –
I
N
S
T
A
L
L
A
T
I
O
N
® ®
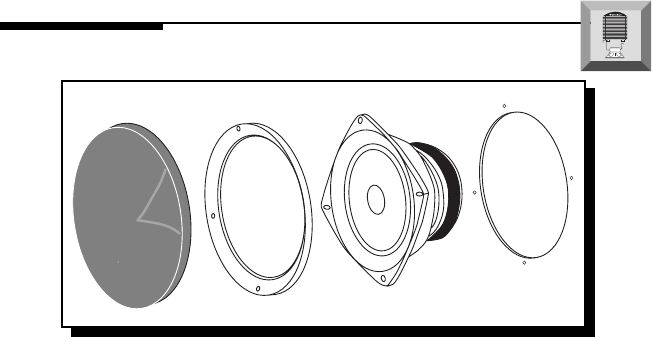
1. Cut the proper size hole for the midrange/woofer.
• For the FNX-1404, cut an 90.48mm (3
9
⁄16") diameter hole
• For the FNX-1405, cut a 113.50mm (4
15
⁄32") diameter hole
• For the FNX-1406F, cut a 127mm (5") diameter hole
• For the FNX-1406, cut a 139.06mm (5
1
⁄2") diameter hole
2. Place the mounting ring over the mounting hole and mark the location of
the screw mounting holes.
3. Remove the ring. Drill the holes for the screws using a 1/8" drill bit.
4. Route the wire through the hole.
5. Place the mounting ring over the hole.
6. Attach the wires and be sure to observe the proper speaker polarity.
7. Place the speaker into the hole and screw the speaker into place. Be
careful not to bend the speaker frame during this step.
8. Press the speaker grille into the mounting ring.