2000 Feb 09 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
2 × 25 W high efficiency car radio power
amplifier
TDA1563Q
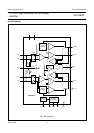
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA1563Q contains two identical amplifiers with
differential inputs. At low output power (up to output
amplitudes of 3 V (RMS) at V
P
= 14.4 V), the device
operates as a normal SE amplifier. When a larger output
voltage swing is needed, the circuit switches to BTL
operation.
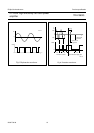
With a sine wave input signal, the dissipation of a
conventional BTL amplifier up to 2 W output power is more
than twice the dissipation of the TDA1563Q (see Fig.10).
In normal use, when the amplifier is driven with music-like
signals, the high (BTL) output power is only needed for a
small percentage of the time. Assuming that a music signal
has a normal (Gaussian) amplitude distribution, the
dissipation of a conventional BTL amplifier with the same
output power is approximately 70% higher (see Fig.11).
The heatsink has to be designed for use with music
signals. With such a heatsink, the thermal protection will
disable the BTL mode when the junction temperature
exceeds 150 °C. In this case, the output power is limited to
5 W per amplifier.
The gain of each amplifier is internally fixed at 26 dB. With
the MODE pin, the device can be switched to the following
modes:
• Standby with low standby current (<50 µA)
• Mute condition, DC adjusted
• On, operation.
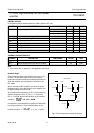
The information on pin 12 (selectable clip) determines at
which distortion figures a clip detection signal will be
generated at the clip output. A logic 0 applied to pin 12 will
select clip detection at THD = 10%, a logic 1 selects
THD = 2.5%. A logic 0 can be realised by connecting this
pin to ground. A logic 1 can be realised by connecting it to
V
logic
(see Fig.7) or the pin can also be left open. Pin 12
may not be connected to V
P
because its maximum input
voltage is 18 V (V
P
> 18 V under load dump conditions).
The device is fully protected against a short circuit of the
output pins to ground and to the supply voltage. It is also
protected against a short circuit of the loudspeaker and
against high junction temperatures. In the event of a
permanent short circuit to ground orthe supply voltage, the
output stage will be switched off, causing low dissipation.
With a permanent short circuit of the loudspeaker, the
output stage will be repeatedly switched on and off. In the
‘on’ condition, the duty cycle is low enough to prevent
excessive dissipation.
To avoid plops during switching from ‘mute’ to ‘on’ or from
‘on’ to ‘mute/standby’ while an input signal is present, a
built-in zero-crossing detector only allows switching at
zero input voltage. However, when the supply voltage
drops below 6 V (e.g. engine start), the circuit mutes
immediately, avoiding clicks from the electronic circuit
preceding the power amplifier.
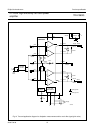
The voltage of the SE electrolytic capacitor (pin 4) is kept
at 0.5V
P
by a voltage buffer (see Fig.1). The value of this
capacitor has an important influence on the output power
in SE mode. Especially at low signal frequencies, a high
value is recommended to minimize dissipation.
The two diagnostic outputs (clip and diag) are
open-collector outputs and require a pull-up resistor.
The clip output will be LOW when the THD of the output
signal is higher than the selected clip level (10% or 2.5%).
The diagnostic output gives information:
• about short circuit protection:
– When a short circuit (to ground or the supply voltage)
occurs at the outputs (for at least 10 µs), the output
stages are switched off to prevent excessive
dissipation. The outputs are switched on again
approximately 50 ms after the short circuit is
removed. During this short circuit condition, the
protection pin is LOW.
– When a short circuit occurs across the load (for at
least 10 µs), the output stages are switched off for
approximately 50 ms. After this time, a check is made
to see whether the short circuit is still present.
The power dissipation in any short circuit condition is
very low.
• during startup/shutdown, when the device is internally
muted.
• temperature detection: Thissignal (junction temperature
> 145°C) indicates that the temperature protection will
become active. The temperature detection signal can be
used to reduce the input signal and thus reduce the
power dissipation.