How to operate the Sound Adjustment Mode
39
X
How to operate the Sound Adjustment Mode
About Sound Adjustment Mode
This equipment is equipped with various functions to compensate the acoustic characteristics inside
the vehicle.
The following adjustments can be made in the sound adjustment mode.
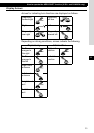
• Crossover (FRONT/REAR/NON-FADER)
• Switching the non fader phase.
Crossover
The frequency band that is stored by audio media such as CDs is a fairly wide range from 20 Hz to 20
kHz, and it is difficult for a single speaker to be able to play back all frequencies in such a wide range.
Because of this, several speakers can be used, with different frequency bands (such as treble,
medium and bass) allotted to each speaker so that wide frequency ranges can be played back.
The "Crossover" function is used to allot the frequency ranges that are to be played back by each
speaker in accordance with the installed speaker and the layout of the speakers, in order to obtain
the maximum level of performance from the speakers and to provide the most stable frequency
characteristics.
The crossover function includes a high-pass filter (HPF) for playing back treble sounds, and a low-
pass filter (LPF) for playing back bass sounds. In addition, the HPF and LPF are used in
combination in order to play back sounds in the medium range.
For example, when adjusting the HPF, frequencies that are lower than the specified frequency are
progressively dampened, rather than simply not being played back at all. The "slope" adjustment
function is the function that is used to adjust these dampening characteristics.
The slope characteristics of a filter are such that with larger slope values (for example 12 dB/oct),
the slope becomes steeper, and so the amount of sound mixing in with neighboring bands becomes
less so that only the target band is played back. However, it also causes the merging of sound
between speakers to become poorer and can result in greater distortion.
• The crossover function is a filter that allocates specified frequency bands.
• A high-pass filter (HPF) is a filter that cuts out frequencies that are lower than the specified
frequency (bass range) and allows higher frequencies (treble range) to pass through.
• A low-pass filter (LPF) is a filter that cuts out frequencies that are higher than the specified
frequency (treble range) and allows lower frequencies (bass range) to pass through.
• The slope is the signal level at which frequencies that are one octave higher or one octave lower
are dampened.
The larger the slope value, the greater the slope. In addition, when "PASS" is selected, the slope
is eliminated (sound does not pass through the filters), so that the crossover function has no
effect.
fc1(LPF) fc2(HPF) fc3(LPF) fc4(HPF)
20kHz
-3dB
Bass range Mid range Treble range
20Hz
fc*: Cutoff frequency
IX