NI-DSP Analysis VI Reference Chapter 2
Part 3: NI-DSP Function Reference 2-14 NI-DSP SRM for LabVIEW for Windows
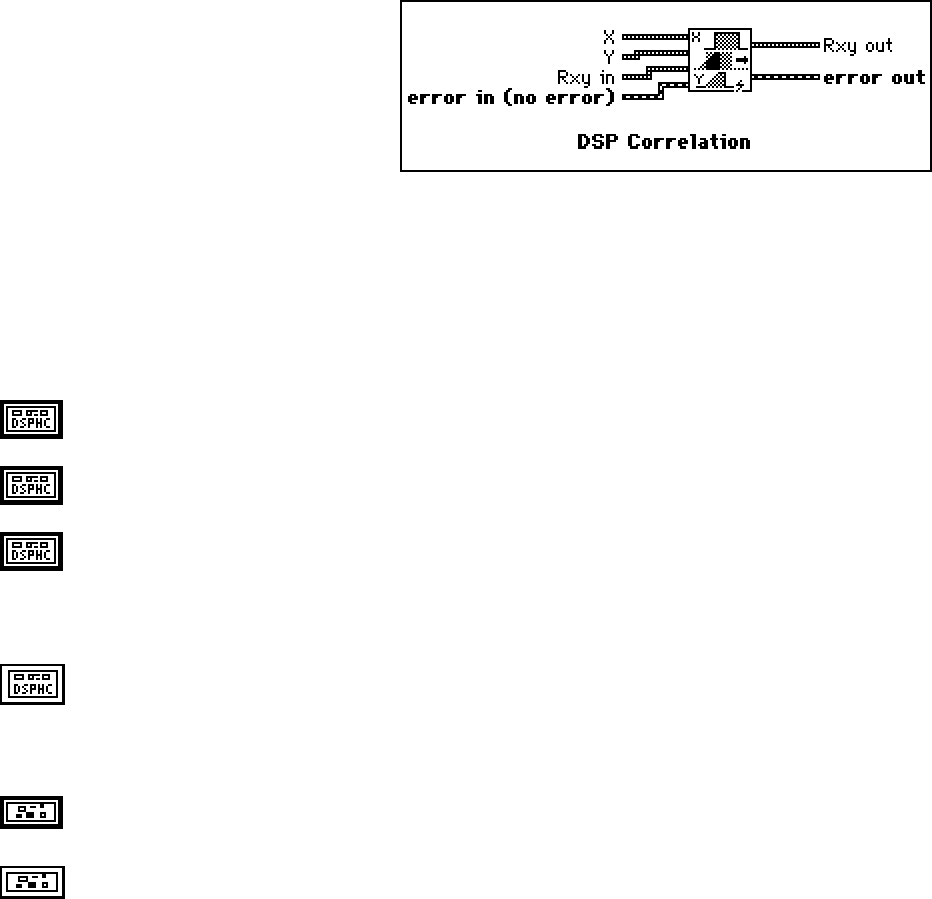
DSP Correlation
Computes the cross correlation of the input
sequences X and Y. The cross correlation R
xy
(t)
of the signals x(t) and y(t) is defined as follows:
R
xy
(t) = x(t) ⊗ y(t) =
∫
-∞
∞
x(t) y(t+t) dt ,
where the symbol ⊗ denotes correlation.
For the discrete implementation of the correlation, let R
xy
represent the output sequence X ⊗ Y, n be the number of
elements in the input sequence X, and m be the number of elements in the input sequence Y. You then obtain the
elements of R
xy
using the following formula:
R
xy i
=
∑
k=0
n-1
x[k] y[k+m-1] for i = 0, 1, 2, …, m+n-1 ,
X is a DSP Handle Cluster that indicates the memory buffer on the DSP board that contains the input
signal array X.
Y is a DSP Handle Cluster that indicates the memory buffer on the DSP board that contains the input
signal array Y.
Rxy in is a DSP Handle Cluster that indicates the memory buffer on the DSP board that will contain the
correlation results.
Note: The size of Rxy in must be at least (n+m-1) elements long. n is the size of X, m is the size
of Y.
Rxy out is a DSP Handle Cluster that is identical to the Rxy in, but with the correlation of X and Y
already stored in the memory buffer on the DSP board.
Note: If X and Y are the same array, an auto correlation is performed, otherwise, a cross correlation is
performed. You cannot perform the operation in place.
error in (no error) contains the error information from a previous VI. If an error occurs, it is passed out
error out and no other calls are made.
error out contains the error information for this call.


















