Chapter 5
Configuring the Wireless-G Router
12
Wireless-G VPN Router with RangeBooster
Setup > Advanced Routing
Setup > Advanced Routing
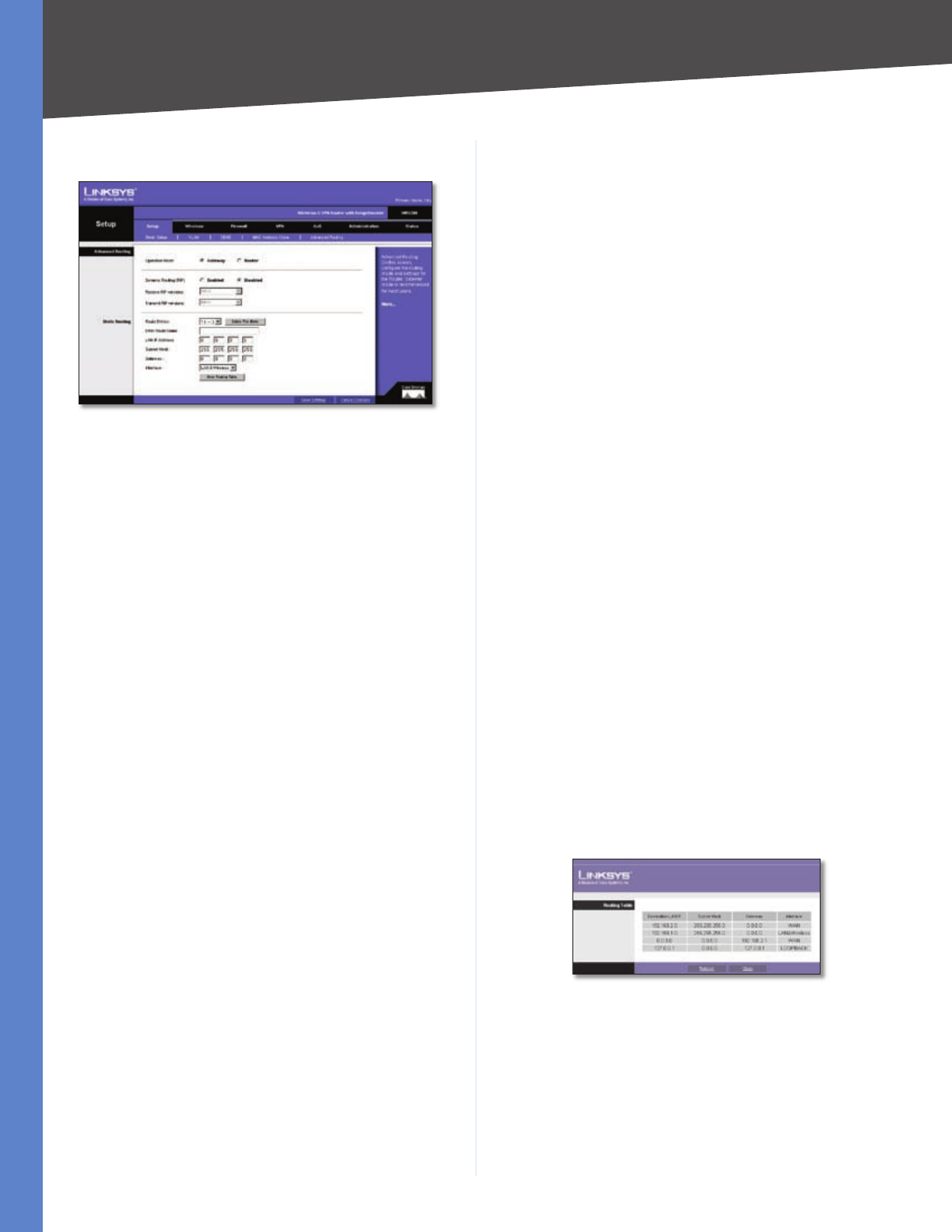
The Setup > Advanced Routing screen allows you to
configure the dynamic and static routing settings.
Operation Mode Select Gateway or Router from the
drop-down menu. If this Router is hosting your network’s
connection to the Internet, keep the default, Gateway,
which will also enable NAT. If you have a different router
hosting your Internet connection, then select Router.
Dynamic Routing
With Dynamic Routing you can enable the Router to
automatically adjust to physical changes in the network’s
layout. The Router, using the RIP protocol, determines
the network packets’ route based on the fewest number
of hops between the source and the destination. The RIP
protocol regularly broadcasts routing information to other
routers on the network.
Dynamic Routing (RIP) To use dynamic routing, click the
Enabled radio button.
Receive RIP Versions To use dynamic routing for
reception of network data, select the protocol you want:
RIPv1 or RIPv2.
Transmit RIP Versions To use dynamic routing for
transmission of network data, select the protocol you
want: RIPv1 or RIPv2.
Static Routing
If the Router is connected to more than one network,
you can configure static routes to direct packets to the
destination network (A static route is a pre-determined
pathway that a packet must travel to reach a specific host
or network.) To create a static route, change the following
settings:
Route Entries Select the number of the static route from
the drop-down menu. The Router supports up to 5 static
route entries.
Delete This Entry If you need to delete a route, select its
number from the drop-down menu, and click Delete This
Entry.
Enter Router Name Enter the name of your Router.
LAN IP Address The LAN IP Address is the address of the
remote network or host to which you want to assign a
static route. Enter the IP address of the host for which you
wish to create a static route. If you are building a route to
an entire network, be sure that the network portion of the
IP address is set to 0. For example, the Router’s standard IP
address is 192.168.1.1. Based on this address, the address
of the routed network is 192.168.1, with the last digit
determining the Router’s place on the network. Therefore
you would enter the IP address 192.168.1.0 if you wanted
to route to the Router’s entire network, rather than just to
the Router.
Subnet Mask The Subnet Mask (also known as the
Network Mask) determines which portion of an IP address
is the network portion, and which portion is the host
portion. Take, for example, a network in which the Subnet
Mask is 255.255.255.0. This determines (by using the values
255) that the first three numbers of a network IP address
identify this particular network, while the last digit (from 1
to 254) identifies the specific host.
Gateway Enter the IP address of the gateway device that
allows for contact between the Router and the remote
network or host.
Interface Select LAN & Wireless or Internet, depending
on the location of the static route’s final destination.
Show Routing Table Click the Show Routing Table
button to open a screen displaying how packets are
routed through your local network. For each route, the
Destination LAN IP address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, and
Interface are displayed. Click Refresh to update the
information. Click Close to exit this screen.
Setup > Advanced Routing
When you have finished making changes to the screen,
click Save Settings to save the changes, or click Cancel
Changes to undo your changes. For help information,
click More.
