CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
6-4.
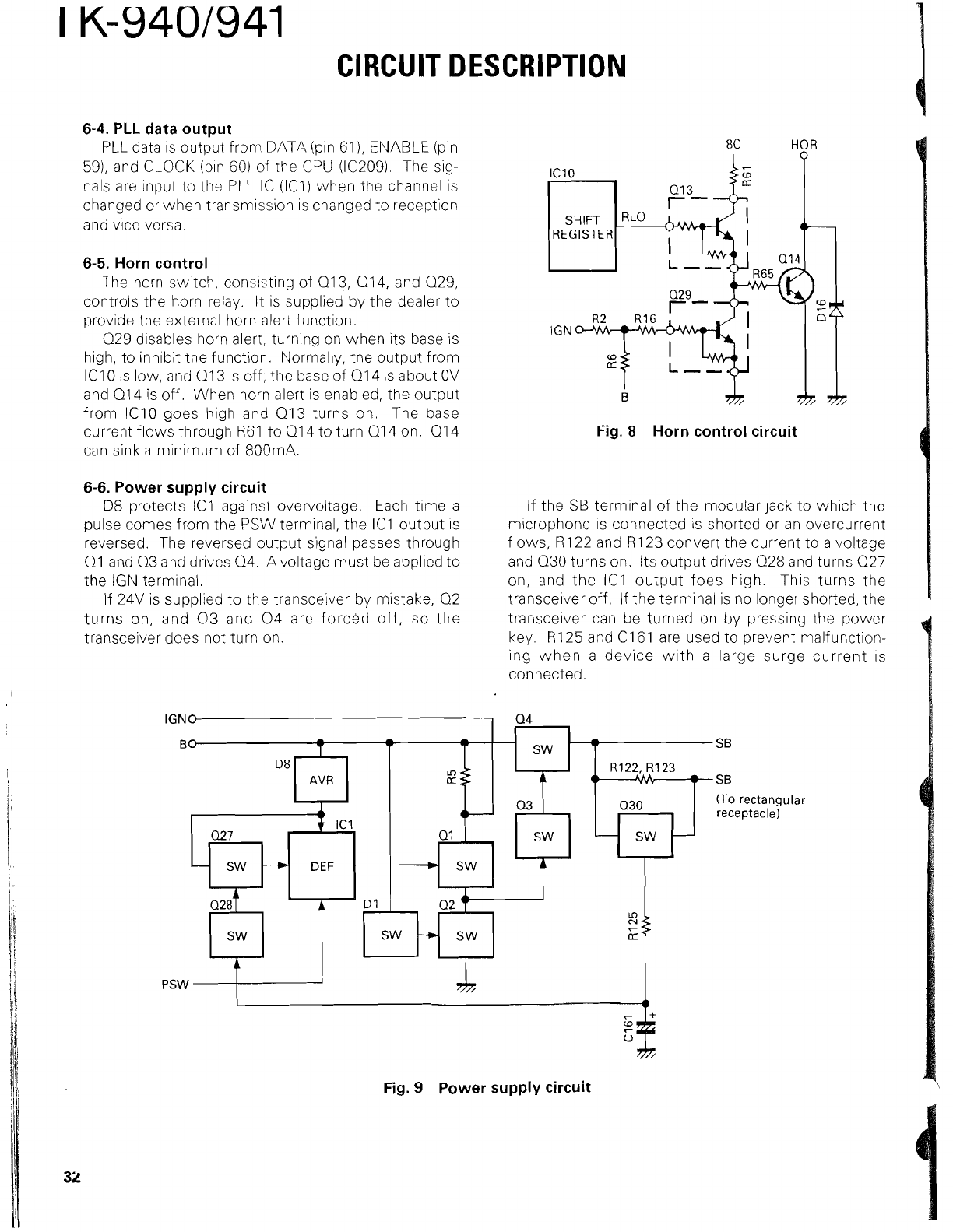
PLL data output
PLL data is output
fronl DATA (pin 61
),
EIUABLE (pin
8c
HOR
591, and CLOCK (p~n
60)
of the CPU (IC2091. The sig-
nas are input to the PLL IC (ICli when the channel is
01 3
changed or when transmission is changed to reception
and vice versa.
6-5.
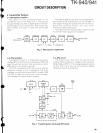
Horn control
014
The horn switch, consisting of Q13, 014, and Q29,
controls the horn relay. It is supplied by the dealer to
Q29-
provide the external horn alert function.
R2 R16
r
IGN
029 disables horn alert, turning on when its base is
high, to
inh~bit the function. Normally, the output from
lClO is low, and 013 is off; the baseof 014 is about OV
and 014 is off. When horn alert is enabled, the output
from
lClO goes high and Q13 turns on. The base
current flows through
RE1 to Q14 to turn Q14 on. Q14
Fig.
8
Horn control circuit
can sink
a
minimum of 800mA.
6-6.
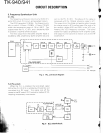
Power supply circuit
D8 protects
1C1 against overvoltage. Each time a
pulse comes from the PSW terminal, the
IC1 output is
reversed. The reversed output signal passes through
01 and Q3 and drives
04. A voltage must be applied to
the
IGN
terminal.
If 24V is supplied to the transceiver by mistake,
Q2
turns on, and 03 and 04 are forced off,
so the
transceiver does not turn on.
If the
SB
terminal of the modular jack to which the
microphone is connected
is shorted or an overcurrent
flows,
R122 and R123 convert the current to a voltage
and
030 turns on. Its output drives 028 and turns Q27
on, and the
IC1 output foes high. This turns the
transceiver off. If the terminal is no longer shorted, the
transceiver can be turned on by pressing the power
key.
R125andC161 are used to prevent malfunction-
ing when a device with a large surge current is
connected.
Fig.
9
Power supply circuit
BO
1
T
-
SW
-
SB
D8
LO
R122, R123
AVR
LT
4)
vAvA,
=
SB
I
03 030
a+
IC1
(To
rectangular
receptacle)
Q27 01
SW
-
SW
-
-
SW
DEF
SW
PSW