Design Features
1-2
Introduction
1.1 Design Features
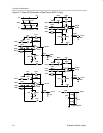
The EVM board design allows many circuits to be constructed easily and
quickly. There are three circuit development areas on the board, and each
uses IC amplifiers in the SOIC package. Area 100 is for a single operational
amplifier (op amp), with or without shutdown. It also features offset nulling pin
pads. Area 200 is for a dual op amp, with or without shutdown. Area 300 is for
a quad op amp, with or without shutdown. A few possible circuits include:
Voltage follower
Noninverting amplifier
Inverting amplifier
Simple or algebraic summing amplifier
Difference amplifier
Current to voltage converter
Voltage to current converter
Integrator/low-pass filter
Differentiator/high-pass filter
Instrumentation amplifier
Sallen-Key filter
The EVM PCB is of two-layer construction, with a ground plane on the solder
side. Circuit performance should be comparable to final production designs.
1.2 Power Requirements
The devices and designs that are used dictate the input power requirements.
Three input terminals are provided for each area of the board:
Vx+ Positive input power for area x00 i.e., V1+ ⇒ area 100
GNDx Ground reference for area x00 i.e., GND2 ⇒ area 200
Vx– Negative input power for area x00 i.e., V3– ⇒ area 300
Each area has four bypass capacitors – two for the positive supply, and two
for the negative supply. Each supply should have a 1-µF to 10-µF capacitor for
low-frequency bypassing and a 0.01-µF to 0.1-µF capacitor for high-frequency
bypassing.
When using single-supply circuits, the negative supply is shorted to ground by
bridging C104 or C105 in area 100, C209 or C210 in area 200, or C311 or C312
in area 300. Power input is between Vx+ and GNDx. The voltage reference
circuitry is provided for single-supply applications that require a reference
voltage to be generated.