22
User's Guide HDSP System Multiface II © RME
12. Operation and Usage
12.1 Playback
The HDSP system can play back audio data only in supported modes (channels, PCM) and
formats (sample rate, bit resolution). Otherwise an error message appears (for example at 22
kHz and 8 bit).
In the audio application being used, HDSP must be selected as output device. This can often be
found in the Options, Preferences or Settings menus under Playback Device, Audio Devices,
Audio etc.
We strongly recommend switching off all system sounds (via >Control Panel /Sounds<). Also
HDSP should not be the Preferred Device for playback, as this could cause loss of synchroniza-
tion and unwanted noises. If you feel you cannot do without system sounds, you should con-
sider buying a cheap Blaster clone and select this as Preferred Device in >Control Panel
/Multimedia /Audio<.
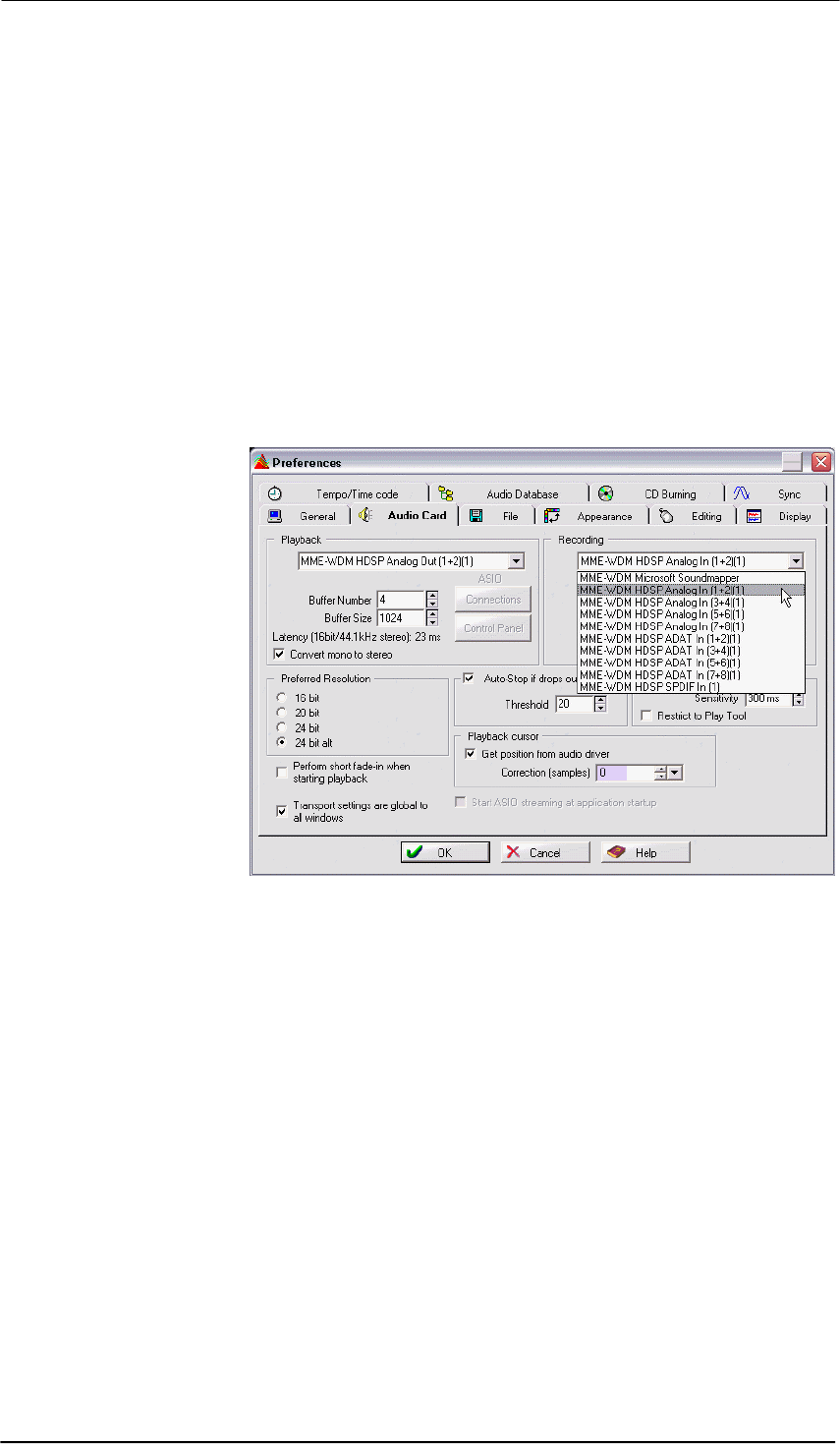
The screenshot shows a
typical configuration dialog
of a (stereo) wave editor.
After selecting a device,
audio data is sent to an
analog or digital (ADAT /
SPDIF) port, depending
on which has been se-
lected as playback device.
Increasing the number
and/or size of audio buff-
ers may prevent the audio
signal from breaking up,
but also increases latency
i.e. output is delayed. For
synchronized playback of
audio and MIDI (or simi-
lar), be sure to activate the
checkbox ‘Get position
from audio driver’.
The HDSP system’s ADAT optical interface allows sample rates of up to 96 kHz using a stan-
dard ADAT recorder. Single-channel data at this frequency requires two ADAT channels,
achieved using the Sample Multiplexing technique. This reduces the number of available ADAT
channels from 8 to 4. Under Windows MME, channels are routed to ADAT devices in double-
speed mode as follows:
• Only stereo pairs (1+2) and (3+4) of the ADAT port are available
This kind of implementation allows a problem-free usage of the ADAT port in both Single and
Double Speed, as the routing doesn't change. However, the hardware spreads the data differ-
ently: Channel 1 is transmitted via channels 1 and 2, channel 2 via 3 and 4 etc.
Please refer to the diagram in chapter 18.2. Routing for record and playback is identical.


















