22 DXZ948RMP
English
No.
Parametric Equalizer Parameters
(car type)
Channel
Band 1 Band 2 Band 3
FGQF GQFGQ
1 Front 250 Hz -8 dB 3 2 kHz -4 dB 1 5 kHz -4 dB 1
(SEDAN-1) Rear 250 Hz -10 dB 3 1.25 kHz 0 dB 5 8 kHz 0 dB 5
2 Front 250 Hz -10 dB 7 800 Hz -4 dB 3 8 kHz -5 dB 1
(SEDAN-2) Rear 80 Hz 3 dB 7 125 Hz -12 dB 5 1.25 kHz 0 dB 5
3 Front 250 Hz -8 dB 3 1 kHz -8 dB 3 10 kHz -6 dB 1
(WAGON-1) Rear 250 Hz -8 dB 3 800 Hz -8 dB 1 8 kHz 0 dB 5
4 Front 250 Hz -8 dB 7 400 Hz -10 dB 7 1.25 kHz -8 dB 7
(WAGON-2) Rear 125 Hz -8 dB 3 500 Hz -5 dB 5 1.6 kHz 0 dB 3
5 Front 125 Hz -4 dB 5 1.25 kHz -4 dB 3 2 kHz 3 dB 7
(MINI VAN-1) Rear 250 Hz -6 dB 1 630 Hz -4 dB 3 8 kHz 0 dB 5
6 Front 250 Hz -4 dB 3 1.25 Hz -8 dB 3 80 Hz 3 dB 3
(MINI VAN-2) Rear 250 Hz -8 dB 3 500 Hz -5 dB 5 8 kHz 0 dB 5
AC-Processor III Operations
Q curve : 20 Q curve : 1
Q curve : (Q)
FREQUENCY (centre frequency selection)
Selects the frequency to be used as the centre
of the frequency band to be compensated from
the range 20Hz to 20kHz.
(1/3 octave steps, 31 points)
GAIN (gain adjustment)
Adjusts the gain (output level) within the range
-12dB to +12dB.
(1dB steps, 25 points)
Q (Q curve selection)
Sets one of 1, 3, 5, 7, or 20 as the sharpness of
the Q curve.
● Compensation
There is no need to compensate frequency
characteristics if they are flat (no peaks or
valleys) when you have measured the
frequency characteristics with a measuring
device. However, sometimes the frequency
characteristics rise or fall in some places. If this
happens, the frequency characteristics must be
compensated. Create a frequency curve having
characteristics that are opposite to the centre
frequency of parts where the characteristics rise
and fall to cancel out these peaks and values,
and make the frequency characteristics as flat
as possible.
Making the frequency characteristics as flat as
possible is called “compensation.”
On this unit, frequency characteristics can be
compensated by P.EQ (Parametric Equalizer).
● Compensation of frequency
characteristics
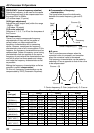
The figure below shows the relationship
between the centre frequency, gain and Q
curve.
3dB
Q =
F
f
f
● Q curve
The Q curve becomes sharper when the
numerical value is increased, and smoother
when the numerical value is decreased.
Flat frequency characteristics can be made by
selecting a Q curve opposite to that of the curve
to be compensated.
F: Centre frequency, G: Gain (output level), Q: Q curve
Level
(dB)
Gain
(G)
Center Frequency (F)
Frequency
(Hz)
Q curve (Q)
Frequency
curve