Garmin GPSMAP 695/696 Owner’s Manual
190-00919-00 Rev. F
7
Overview
Overview GPS Navigation Flight Planning Hazard Avoidance Additional Features Appendices Index
ACQUIRING SATELLITES
When the receiver is in the process of acquiring enough satellite signals for navigation,
the receiver uses satellite orbital data (collected continuously from the satellites) and last
known position to determine the satellites that should be in view. ‘Acquiring Satellites’
is indicated as the solution until a sufficient number of satellites have been acquired for
computing a solution.
When the receiver is in the process of acquiring a 3D differential GPS solution, ‘3D GPS
Location’ is indicated as the solution until the 3D differential fix has finished acquisition.
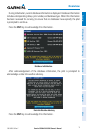
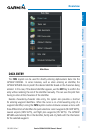
SATELLITE INFORMATION
Satellites currently in view are shown at their respective positions on a satellite
constellation diagram. The outer circle of the constellation diagram represents the horizon,
the inner circle represents 45° above the horizon, and the center point shows the position
directly overhead. Each satellite is represented by a square containing the Pseudo-Random
Noise (PRN) number (i.e., satellite identification number).
The INFO Page can be helpful in troubleshooting weak (or missing) signal levels due to
poor satellite coverage or installation problems. As the GPS receiver locks onto satellites, a
signal strength bar is displayed for each satellite in view, with the appropriate satellite PRN
number (01-32 or 33-64 for WAAS) below each bar. The progress of satellite acquisition is
shown in three stages, as indicated by signal bar appearance:
-Nobar—Receiverislookingfortheindicatedsatellite
-Graybar—Receiverhascollectedthenecessarydataandthesatellitesignalcan
be used
-Greenbar—SatelliteisbeingusedfortheGPSsolution