15 - 5
15. ABSOLUTE POSITION DETECTION SYSTEM
15.5 Signal explanation
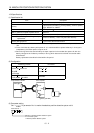
When the absolute position data is transferred, the signals of connector CN1 change as described in this
section. They return to the previous status on completion of data transfer. The other signals are as
described in Section 3.3.2.
For the I/O interfaces (symbols in the I/O Category column in the table), refer to Section 3.6.
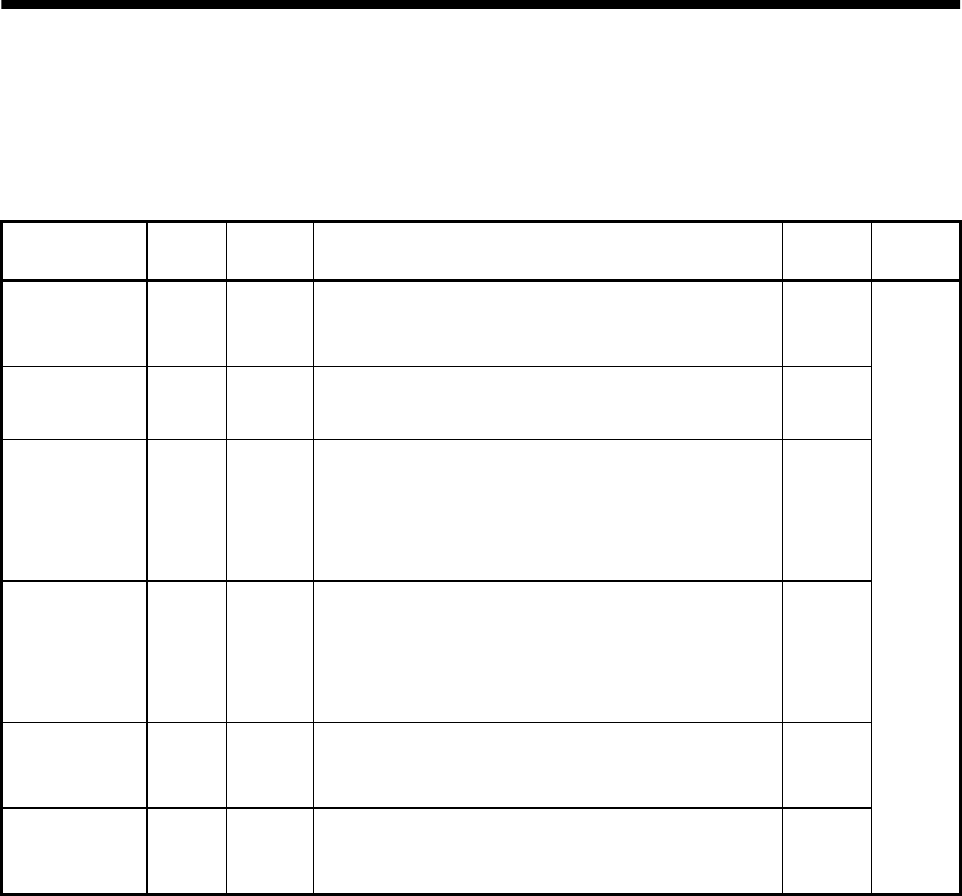
Signal name Code Pin No. Function/Application
I/O
category
Control
mode
ABS transfer
mode
ABSM
(Note)
CN1B-8
While ABSM is shorted by connection to SG, the servo
amplifier is in the ABS transfer mode, and the functions
of ZSP, TLC, and D01 are as indicated in this table.
DI-1
ABS request ABSR
(Note)
CN1B-9
ABSR-SG are shorted to request the ABS data in the
ABS transfer mode.
DI-1
ABS bit 0 D01 CN1B-4
Indicates the lower bit of the ABS data (2 bits) which is
sent from the servo to the programmable controller in
the ABS transfer mode.
If there is a signal, the circuit between D01 and SG is
closed.
DO-1
ABS bit 1 ZSP CN1B-19
Indicates the upper bit of the ABS data (2 bits) which is
sent from the servo to the programmable controller in
the ABS transfer mode.
If there is a signal, the circuit between ZSP and SG is
closed.
DO-1
Send data ready TLC CN1B-6
Indicates that the data to be sent is being prepared in
the ABS transfer mode. At the completion for the ready
state, the circuit between TLC and SG is closed.
DO-1
Home position
setting
CR CN1A-8
When CR-SG are shorted, the position control counter is
cleared and the home position data is stored into the
non-volatile memory (backup memory).
DI-1
P
(Position
control)
Note: When "Used in absolute position detection system" is selected in parameter No. 1, pin CN1B-8
acts as the ABS transfer mode (ABSM) signal and pin CN1B-9 as the ABS request (ABSR) signal.
They do not return to the original signals if data transfer ends.