TELEDYNE INSTRUMENTS
Theory of Operation 460L Instruction Manual
56 05228 Rev B
PRINTED DOCUMENTS ARE UNCONTROLLED DCN 5164
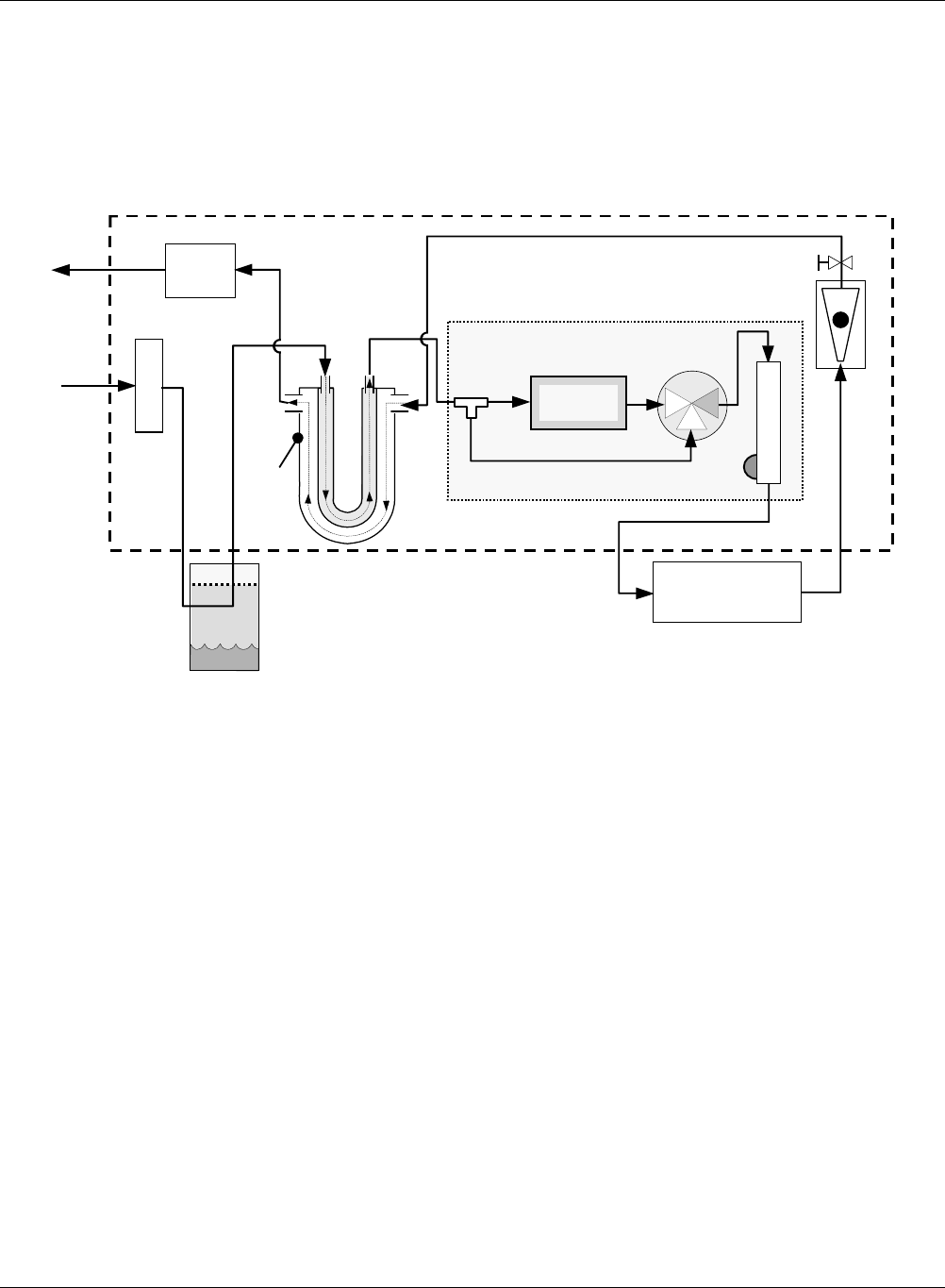
10.2.3. Optional Sample Conditioning
The source air measured by the 460L needs to be as dry as possible. Significant amounts of liquid
or vaporous water present in the source gas can foul the measurement cell optics. Also, water
absorbs O
3
and interferes with the 460L’s ability to accurately measure the O
3
in the source gas.
To counteract this problem, several optional components can be added to the 460L.
O
3
Measurement Cell
Particulate Filter
Flow Meter
MEASURE
REFERENCE
VALVE
O
3
IN
Exhaust
Out
Monitor Enclosure
PUMP
Flow Meter Valve
1
3
2
O
3
Scrubber
O
3
DESTRUCT
(Optional)
H
2
O Vapor Dryer
(Optional)
Vapor
Dryer
Purge
Line
Gas
Pressure Sensor
ABSORPTION TUBE
H
2
O
Coalescing
Filter
(Optional)
Figure 10-4 460L Internal Pneumatic Diagram with Optional Sample Conditioning
10.2.3.1. H
2
O Coalescing Filter
The first step of this drying process is to remove any liquid water from the source gas. The 460L
uses a Teflon
®
membrane, coalescing filter to accomplish this. This filter works in two ways. First,
droplets of water that are large enough to precipitate out of the air on their own simply fall to the
bottom of the filters container. Second, smaller droplets, small enough to stay combined and
bourn along with the air encounter the Teflon
®
membrane (47 mm diameter; 20 micron pore size)
at the top of the filter, and because Teflon
®
is inherently water repellent, these tiny droplets
collect along the Teflon
®
fibers combining and growing until they are large enough to drip down
into the reservoir.
10.2.3.2. H
2
O Vapor Dryer
Once all of the liquid water is removed from the source gas, a separate, Perma Pure
®
single tube
permeation tube dryer removes any vaporous water still present. The dryer consists of a single
tube of Nafion
®
, a co-polymer similar to Teflon
®
that absorbs water very well but not other
chemicals. The Nafion
®
tube is mounted within an outer, flexible plastic tube. As gas flows
through the inner Nafion
®
tube, water vapor is absorbed into the membrane walls. The absorbed
water is transported through the membrane wall and evaporates into the dry purge gas flowing
through the outer tube, countercurrent to the gas in the inner tube. This process is called
pervaporation and is driven by the humidity gradient between the inner and outer tubes as well as
the flow rates and pressure difference between inner and outer tubing.