7 - 8
7. GENERAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT
(c)Adjustment description
1) Speed control gain 2 (parameter No. 37)
This parameter determines the response level of the speed control loop. Increasing this value
enhances response but a too high value will make the mechanical system liable to vibrate. The
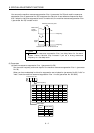
actual response frequency of the speed loop is as indicated in the following expression:
Speed loop response
frequency(Hz)
Speed control gain 2 setting
(1 ratio of load inertia moment to servo motor inertia moment)
2
2) Speed integral compensation (VIC: parameter No. 38)
To eliminate stationary deviation against a command, the speed control loop is under
proportional integral control. For the speed integral compensation, set the time constant of this
integral control. Increasing the setting lowers the response level. However, if the load inertia
moment ratio is large or the mechanical system has any vibratory element, the mechanical
system is liable to vibrate unless the setting is increased to some degree. The guideline is as
indicated in the following expression:
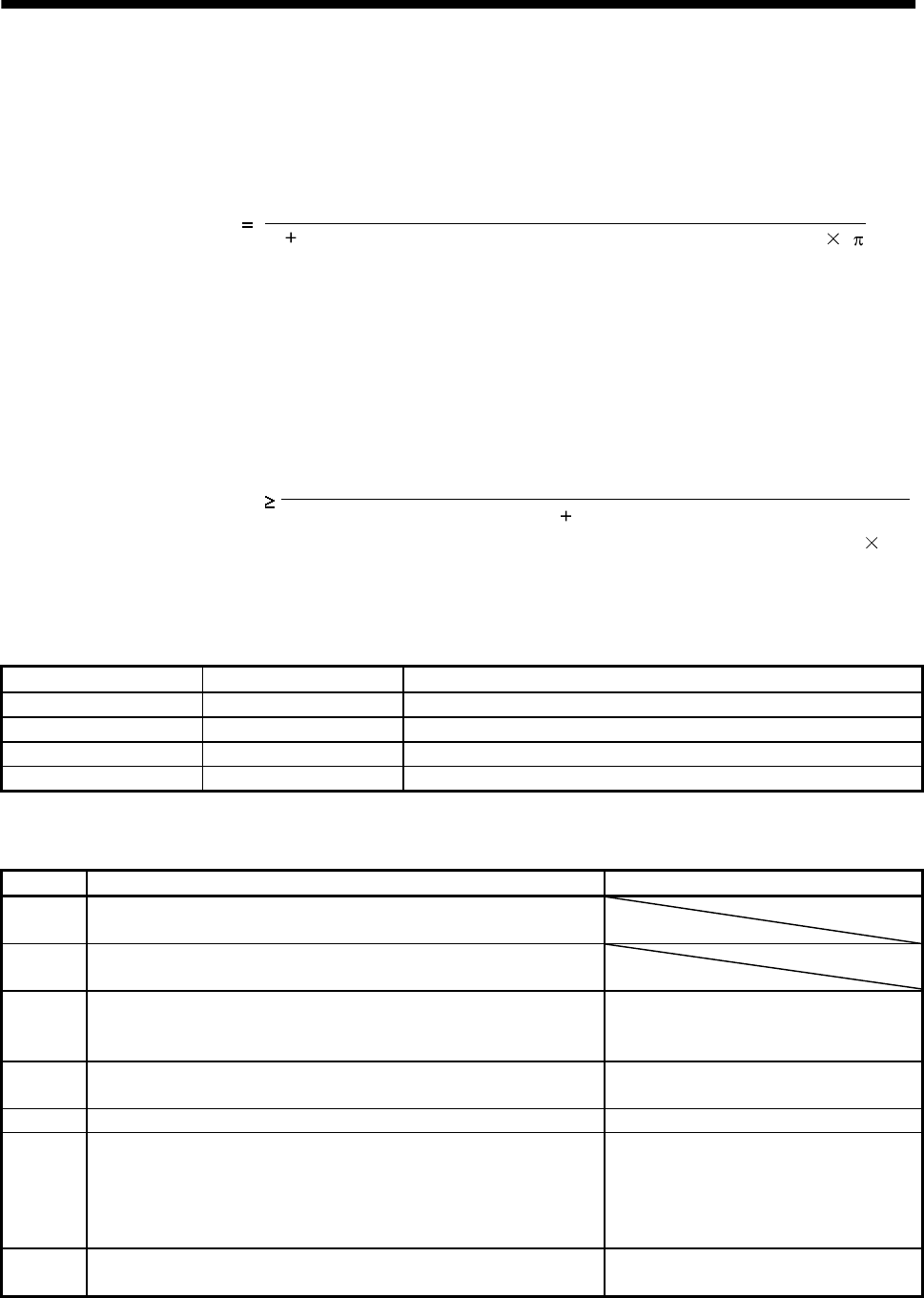
Speed integral compensation
setting(ms)
2000 to 3000
(1 ratio of load inertia moment to
servo motor inertia moment setting 0.1)
Speed control gain 2 setting/
(2) For position control
(a) Parameters
The following parameters are used for gain adjustment:
Parameter No. Abbreviation Name
6PG1Position control gain 1
34 GD2 Ratio of load inertia moment to servo motor inertia moment
37 VG2 Speed control gain 2
38 VIC Speed integral compensation
(b) Adjustment procedure
Step Operation Description
1
Set an estimated value to the ratio of load inertia moment to servo
motor inertia moment (parameter No. 34).
2
Set a slightly smaller value to the position control gain 1 (parameter
No. 6).
3
Increase the speed control gain 2 (parameter No. 37) within the
vibration- and unusual noise-free range, and return slightly if vibration
takes place.
Increase the speed control gain.
4
Decrease the speed integral compensation (parameter No. 38) within
the vibration-free range, and return slightly if vibration takes place.
Decrease the time constant of the speed
integral compensation.
5 Increase the position control gain 1 (parameter No. 6). Increase the position control gain.
6
If the gains cannot be increased due to mechanical system resonance or
the like and the desired response cannot be achieved, response may be
increased by suppressing resonance with adaptive vibration
suppression control or machine resonance suppression filter and then
executing steps 3 to 5.
Suppression of machine resonance.
Refer to Section 8.1.
7
While checking the settling characteristic and rotational status, fine-
adjust each gain.
Fine adjustment