7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS
7 - 4
7.1.2 Adaptive filter II
POINT
The machine resonance frequency which adaptive filter II (adaptive tuning) can
respond to is about 100 Hz to 2.25 kHz. As for the resonance frequency out of
the range, set manually.
When adaptive tuning is executed, vibration sound increases as an excitation
signal is forcibly applied for several seconds.
When adaptive tuning is executed, machine resonance is detected for a
maximum of 10 seconds and a filter is generated. After filter generation, the
adaptive tuning mode automatically shifts to the manual setting.
Adaptive tuning generates the optimum filter with the currently set control gains.
If vibration occurs when the response setting is increased, execute adaptive
tuning again.
During adaptive tuning, a filter having the best notch depth at the set control
gain is generated. To allow a filter margin against machine resonance, increase
the notch depth in the manual setting.
Adaptive vibration suppression control may provide no effect on a mechanical
system which has complex resonance characteristics.
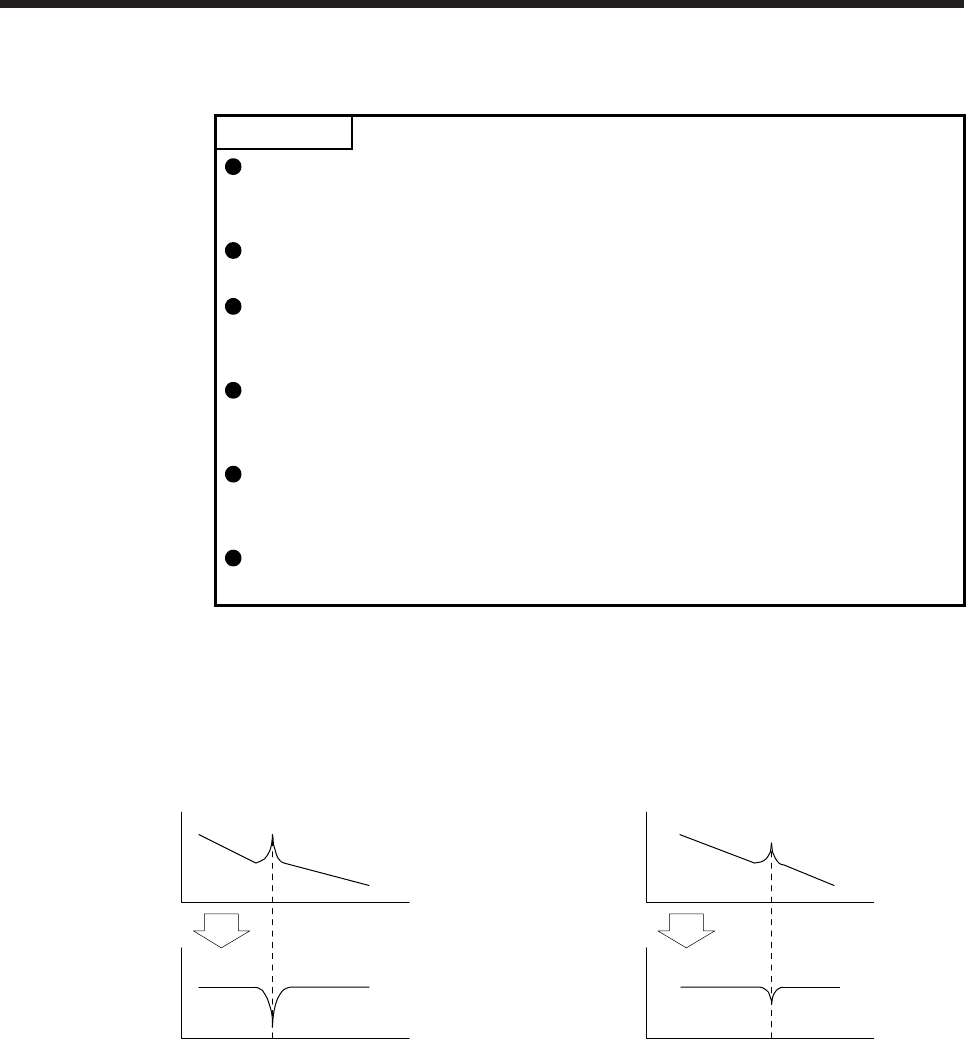
(1) Function
Adaptive filter II (adaptive tuning) is a function in which the servo amplifier detects machine vibration for
a predetermined period of time and sets the filter characteristics automatically to suppress mechanical
system vibration. Since the filter characteristics (frequency, depth) are set automatically, you need not
be conscious of the resonance frequency of a mechanical system.
Response of
mechanical systemNotch depth
Machine resonance point
Notch frequency
Frequency
Frequency
Response of
mechanical systemNotch depth
Machine resonance point
Notch frequency
Frequency
Frequency
When machine resonance is large and
frequency is low
When machine resonance is small and
frequency is high