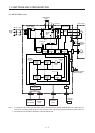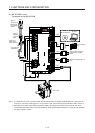
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1 - 6
1.5 Function list
The following table lists the functions of this servo. For details of the functions, refer to each section
indicated in the detailed explanation field.
Function Description
Detailed
explanation
Model adaptive control
This function realizes a high response and stable control following the ideal model.
The two-degrees-of-freedom model adaptive control enables you to set a response to
the command and response to the disturbance separately.
Additionally, this function can be disabled. Refer to section 7.4 to disable this function.
Position control mode This servo amplifier is used as a position control servo.
Speed control mode This servo amplifier is used as a speed control servo.
Torque control mode This servo amplifier is used as a torque control servo.
High-resolution encoder
A high-resolution encoder of 131072 pulses/rev is used as the encoder of the rotary
servo motor compatible with the MELSERVO-JE series.
Absolute position detection
system
Setting a home position once makes home position return unnecessary at every
power-on.
Chapter 12
Gain switching function
You can switch gains during rotation and during stop, and can use input devices to
switch gains during operation.
Section 7.2
Advanced vibration
suppression control II
This function suppresses vibration at the arm end or residual vibration. Section 7.1.5
Machine resonance
suppression filter
This filter function (notch filter) decreases the gain of the specific frequency to
suppress the resonance of the mechanical system.
Section 7.1.1
Shaft resonance suppression
filter
When a load is mounted to the servo motor shaft, resonance by shaft torsion during
driving may generate a mechanical vibration at high frequency. The shaft resonance
suppression filter suppresses the vibration.
Section 7.1.3
Adaptive filter II
The servo amplifier detects mechanical resonance and sets filter characteristics
automatically to suppress mechanical vibration.
Section 7.1.2
Low-pass filter
This function suppresses high-frequency resonance which occurs as servo system
response is increased.
Section 7.1.4
Machine analyzer function
This function analyzes the frequency characteristic of the mechanical system by
simply connecting an MR Configurator2 installed personal computer and servo
amplifier.
MR Configurator2 is necessary for this function.
Robust filter
This function enhances the disturbance response when the response level remains
low because the load to motor inertia ratio of axes, such as a roll feed axis, is high.
[Pr. PE41]
Slight vibration suppression
control
This function suppresses vibration of ±1 pulse generated at a servo motor stop. [Pr. PB24]
Auto tuning
This function automatically adjusts the gain to an optimum value if load applied to the
servo motor shaft varies.
Section 6.3
Regenerative option
Used when the built-in regenerative resistor of the servo amplifier does not have
sufficient regenerative capability for the regenerative power generated.
Section 11.2
Alarm history clear This function clears the alarm history. [Pr. PC21]
Output signal selection
(device settings)
The output devices including MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) and ALM
(Malfunction) can be assigned to certain pins of the CN3 connector.
[Pr. PD07]
Output signal (DO) forced
output
Output signal can be forced on/off independently of the servo status.
Use this function for checking output signal wiring, etc.
Section 4.5.1
(1) (d)
Test operation mode
Jog operation, positioning operation, motor-less operation, DO forced output, and
program operation
MR Configurator2 is necessary for this function.
Section 4.5
MR Configurator2
Using a personal computer, you can perform the parameter setting, test operation,
monitoring, and others.
Section 11.4
One-touch tuning
Gain adjustment is performed just by one click on a certain button on MR
Configurator2.
MR Configurator2 is necessary for this function.
Section 6.2
Tough drive function
This function makes the equipment continue operating even under the condition that
an alarm occurs.
The tough drive function includes two types: the vibration tough drive and the
instantaneous power failure tough drive.
Section 7.3